The Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) proxy service is designed to provide a secure way for remote clients to authenticate using Kerberos when they cannot access Active Directory domain controllers directly. Initially intended for services like DirectAccess and Remote Desktop Gateway, the KDC proxy becomes increasingly important as Microsoft phases out NTLM authentication protocols, necessitating its use for additional remote access services.
To establish Kerberos authentication between a client and the KDC service on the AD domain controller, certain ports need to be open:
- UDP/TCP 88: For Kerberos authentication and to obtain Ticket Granting Tickets (TGT).
- UDP/TCP 464: For changing a user’s password via Kerberos.
Since opening these ports for external users is not secure, the KDC proxy can be implemented on a domain-joined server. This proxy listens for Kerberos requests over HTTPS (TCP/443) from external clients and forwards them securely to the domain controller.
In a scenario where an external user connects to a Remote Desktop Gateway (RDGW) server operating in Kerberos-only mode, they may encounter authentication issues if they cannot authenticate via Kerberos due to NTLM being disabled. The user will receive an RDP error indicating that the requested function is not supported.
To resolve this, the KDC Proxy Service (KPSSVC) must be deployed on the RDGW host. This service requires a valid certificate for encryption and server authentication, with the Extended Key Usage (EKU) extended to include Server Authentication and Kerberos Authentication.
The steps to configure this are as follows:
-
Create a connection URL endpoint for the KDC proxy service:
NETSH http add urlacl url=https://+:443/KdcProxy user="NT authorityNetwork Service" -
Generate a unique GUID and set the certificate thumbprint:
$appguid = [Guid]::NewGuid().ToString("B")$kdccert= "YourCertificateThumbprintHere" -
Bind the certificate to the connection endpoint:
netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash=$kdccert appid=$appguid -
Disable HTTPS client certificate authentication requirements for KDC Proxy operations:
REG ADD "HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesKPSSVCSettings" /v HttpsClientAuth /t REG_DWORD /d 0x0 /f -
Enable password authentication:
REG ADD "HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesKPSSVCSettings" /v DisallowUnprotectedPasswordAuth /t REG_DWORD /d 0x0 /f -
Start the KDC Proxy Service:
Set-Service kpssvc -StartupType AutomaticStart-Service kpssvc -
Allow incoming traffic on TCP port 443:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "KDCProxy TCP_In" -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 443
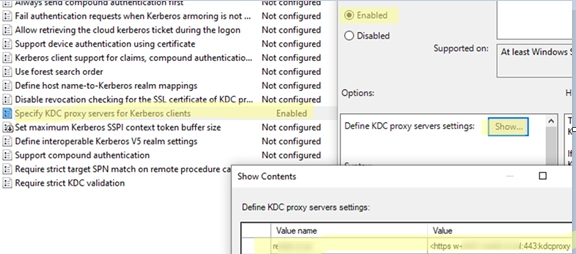
For clients to utilize the KDC proxy for connections, the settings can be applied via Group Policy under Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Kerberos by enabling the "Specify KDC proxy servers for Kerberos clients" policy. The KDC proxy settings can also be set via the registry if preferred.
After configuring the KDC proxy, users can attempt to log in to the RDP gateway, using the proxy to authenticate with the domain controller for a Kerberos ticket. To verify the issuance of a Kerberos ticket via the KDC proxy, users can utilize the command:
klist get krbtgtLogs for the Kerberos proxy authentication can be checked under Event Viewer in the Microsoft -> KDCProxy -> Operational section.
Future Windows releases are expected to simplify KDC proxy deployment through the Windows Admin Center (WAC) web interface.