A common cause of WSUS console connection problems is an overdue cleanup of the server from updates that are no longer needed. In this case, access to the database may time out and the connection is then terminated.
However, the problem could also be due to an expired certificate, although the WSUS console does not provide information on this.
In this case, PowerShell is more informative. Running the command
Get-WsusServer -Name wsus.contoso.com -UseSsl -PortNumber 8531
results in the following error message:
The underlying connection was closed: Could not establish trust relationship for the SSL/TLS secure channel
To confirm that the invalid certificate is causing the connection error, you can open the following URL in your web browser:
https://<WSUS-Server>:8531/selfupdate/wuident.cab
There, you will receive a clear error message and can verify the certificate immediately.
Request a new certificate
If an expired certificate is identified as the root cause, the first step is to issue a new one. As it is common practice to run WSUS on Server Core, the following guide focuses on the PowerShell method. This is, of course, applicable to Windows Server with a desktop interface as well.
In our example, we request the new certificate from a Windows CA. The command using Get-Certificate could look like this:
Get-Certificate -SubjectName "C=DE,O=contoso,CN=wsus,DC=contoso,DC=com" `-DnsName wsus.contoso.com,wsus -Template WebServer `
-CertStoreLocation Cert:LocalMachineMy `
-URL "ldap:///CN=contoso-CA"
Request new SSL certificate for the WSUS server with PowerShell.
The example above issues the certificate for the server wsus.contoso.com using the WebServer template. The second value for the DnsName parameter allows you to connect using the host name wsus only without receiving a certificate warning. You can specify the CA path via the URL parameter.
After successfully obtaining the certificate, it will be located in the store under LocalMachineMy (PersonalCertificates in certlm.msc). You can verify this using the following pattern:
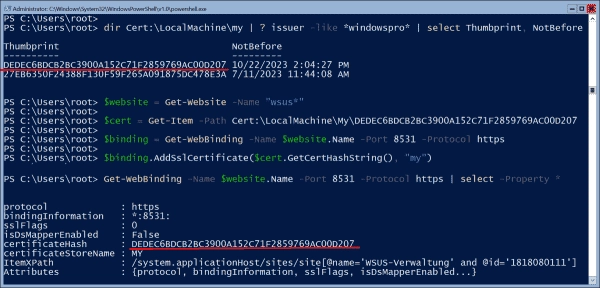
Get-ChildItem Cert:LocalMachineMy | where issuer -like *contoso-CA* |sort -Property NotBefore | select Thumbprint, NotBefore
Next, you’ll need the certificate’s thumbprint to bind it to the WSUS website.
Bind certificate to WSUS site
To activate the new certificate, bind it to the WSUS Administration site in the IIS. This can be done with the following script:
# Store the name of the WSUS website in a variable
$website = Get-Website -Name "wsus*"
# Import the new certificate using the thumbprint
$cert = Get-Item -Path Cert:LocalMachineMyDEDEC6BDCB2BC3900A152…
# Get the current https binding of the WSUS website
$binding = Get-WebBinding -Name $website.Name -Port 8531 -Protocol https
# Assign a new certificate
$binding.AddSslCertificate($cert.GetCertHashString(), "my")
After the successful execution of these commands restart IIS:
Restart-Service w3svc
Bind new SSL certificate to WSUS website.
The new SSL certificate is successfully binded to the WSUS website. This ensures a secure connection and enables your system to prevent any unwanted breaches or security threats.
Now, when you run
Get-WebBinding -Name $website.Name -Port 8531 -Protocol https
it should display the thumbprint of the new certificate, and the WSUS console should be able to connect to the server accordingly.