Category: Windows 11
-

A Guide to Managing Per-User Services in Windows
In Windows, per-user services are specialized services generated for each user during their logon and removed when they log off. They are designed to handle personalized tasks such as search indexing, notifications, and data synchronization, operating within the user account context rather than the LocalSystem context. This concept has been available since Windows 10 and…
-
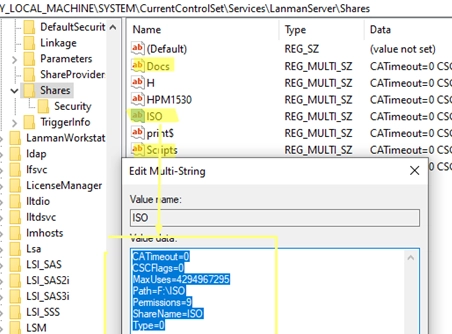
A Step-by-Step Guide to Migrating Your Existing Windows Shares to a New File Server
To migrate existing Windows shares to a new file server, you’ll need to utilize a combination of registry editing and file transfer methods. The shared network folders and their settings are stored under HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesLanmanServerShares in the Windows registry. Step-by-Step Guide for Migration: List Existing Shares:To view current shared SMB resources on a Windows host, use…
-
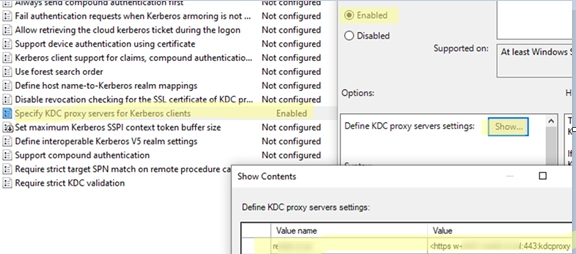
Leveraging KDC (Kerberos) Proxy in Active Directory for Secure Remote Access
The Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC) proxy service is designed to provide a secure way for remote clients to authenticate using Kerberos when they cannot access Active Directory domain controllers directly. Initially intended for services like DirectAccess and Remote Desktop Gateway, the KDC proxy becomes increasingly important as Microsoft phases out NTLM authentication protocols, necessitating…
-

Step-by-Step Guide to Manually Create and Install a Windows Service
In Windows, services operate in the background, allowing applications to run without user interaction and start automatically during boot. This guide walks you through the process of creating a new system service from an executable file using built-in tools available in Windows. To create a service, you can utilize the sc.exe command from the command…
-

Seamless Connectivity: How to Automatically Switch to the Strongest Wi-Fi Network on Windows
Windows 10 and 11 come equipped with a useful AutoSwitch feature, which enables devices to automatically select the Wi-Fi access point (AP) with the strongest signal when multiple APs are broadcasting the same SSID. This functionality helps prevent disconnections due to weak signals by seamlessly connecting to a better option when available. To activate the…
-

Enabling or Disabling VBScript in Windows: A Guide Post-Deprecation
In 2024, Microsoft announced its intention to phase out support for VBScript, a scripting language previously favored for automation in Windows environments due to its simplicity and accessibility. VBScript garnered popularity because it included a built-in Windows runtime and access to a vast library of scripts. However, because of its legacy structure and associated vulnerabilities,…
-
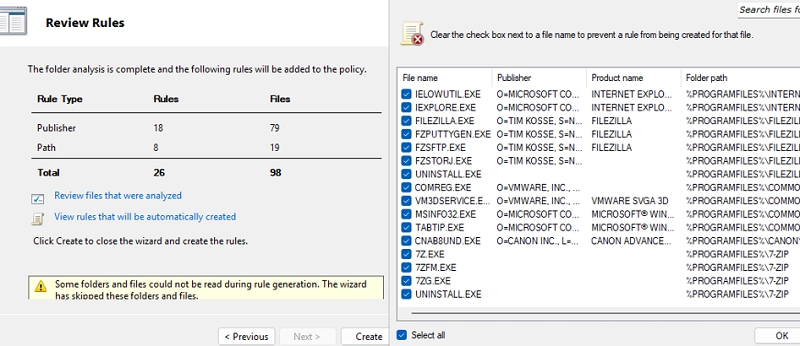
Mastering AppLocker: How to Configure Application Restriction Policies in Windows
Using AppLocker security policies, system administrators can manage which applications run on Windows systems. This tool allows for specific application restrictions, enabling designated user groups to execute applications while blocking others, such as standard users. Initially limited to the Enterprise editions, AppLocker is now accessible in Windows 10 Pro (from version 2004) and all versions…
-

Seamless File Sharing: How to Use SMB over QUIC on Windows Server 2025 Without a VPN
SMB over QUIC is a new feature in Windows Server 2025 that enables users to securely access Windows file shares over the internet without needing a VPN. This functionality, previously available only in the Windows Server 2022 Azure Edition, allows for direct access to SMB file servers from untrusted public networks. The protocol enhances security…
-

How to Recover Your Computer’s Previous Name in Windows: A Step-by-Step Guide
After changing the name of a Windows computer, you might find yourself needing to retrieve its previous name (hostname). This can be accomplished by accessing the Windows registry. To locate the old computer name, navigate to the registry key located at HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftSchedulingAgent. You can either manually check the value of the OldName parameter using the…
-
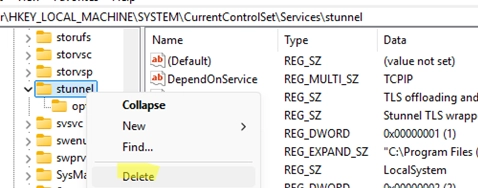
Effortlessly Delete a Windows Service Using CMD or PowerShell: A Step-by-Step Guide
After uninstalling certain programs, it’s not uncommon for leftover services to remain in Windows. This guide will explain how to properly delete a service using the built-in CMD or PowerShell tools, as the Services console (services.msc) only allows basic operations like starting, pausing, or stopping services, but not removing them. Steps to Delete a Windows…