Category: Windows 10
-

How to Load and Initialize Network Drivers in Windows PE or Recovery Environment: A Step-by-Step Guide
This article outlines the process for manually loading and initializing network adapter drivers in Windows PE (Preinstallation Environment) or WinRE (Recovery Environment). These environments are crucial for installing, maintaining, and repairing Windows, as they utilize a streamlined, bootable version of Windows. When booted into WinPE or WinRE, specialized network adapter drivers may not be included,…
-

Customizing Your Drives: A Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Custom Drive Icons in Windows
Customizing drive icons in Windows can enhance navigation and provide a personalized touch to your system. By default, Windows Explorer displays standard icons for local, removable, and mapped network drives. However, you can assign custom icons to make the experience more intuitive. Here’s how to set custom drive icons for various drive types, including steps…
-

A Guide to Managing Per-User Services in Windows
In Windows, per-user services are specialized services generated for each user during their logon and removed when they log off. They are designed to handle personalized tasks such as search indexing, notifications, and data synchronization, operating within the user account context rather than the LocalSystem context. This concept has been available since Windows 10 and…
-
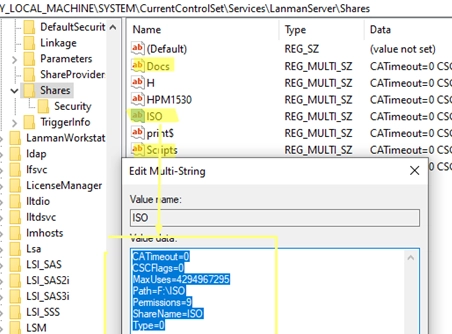
A Step-by-Step Guide to Migrating Your Existing Windows Shares to a New File Server
To migrate existing Windows shares to a new file server, you’ll need to utilize a combination of registry editing and file transfer methods. The shared network folders and their settings are stored under HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesLanmanServerShares in the Windows registry. Step-by-Step Guide for Migration: List Existing Shares:To view current shared SMB resources on a Windows host, use…
-

Seamless Connectivity: How to Automatically Switch to the Strongest Wi-Fi Network on Windows
Windows 10 and 11 come equipped with a useful AutoSwitch feature, which enables devices to automatically select the Wi-Fi access point (AP) with the strongest signal when multiple APs are broadcasting the same SSID. This functionality helps prevent disconnections due to weak signals by seamlessly connecting to a better option when available. To activate the…
-

How to Recover Your Computer’s Previous Name in Windows: A Step-by-Step Guide
After changing the name of a Windows computer, you might find yourself needing to retrieve its previous name (hostname). This can be accomplished by accessing the Windows registry. To locate the old computer name, navigate to the registry key located at HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftSchedulingAgent. You can either manually check the value of the OldName parameter using the…
-
Effortlessly Delete a Windows Service Using CMD or PowerShell: A Step-by-Step Guide
After uninstalling certain programs, it’s not uncommon for leftover services to remain in Windows. This guide will explain how to properly delete a service using the built-in CMD or PowerShell tools, as the Services console (services.msc) only allows basic operations like starting, pausing, or stopping services, but not removing them. Steps to Delete a Windows…
-

Your Guide to Accessing Windows 10 Extended Security Updates After End-of-Life
Support for Windows 10 will come to an end on October 14, 2025, meaning that Microsoft will cease providing technical assistance, feature updates, or security updates for the operating system. This lack of security updates can lead to increased vulnerability to malware, ransomware, and cyberattacks. Users are encouraged to either upgrade to Windows 11 if…
-

Troubleshooting: Windows Stuck at ‘Getting Windows Ready, Don’t Turn Off Your Computer’ Screen
This issue of Windows getting stuck at the "Getting Windows Ready. Don’t turn off your computer" message is fairly common, especially on Windows Server versions (2022, 2019, 2016) and occasionally on Windows 10 and 11. This often occurs after installing updates or modifying system roles and features. When encountering this message, the best initial advice…
-
Optimizing DPI Scaling and Font Size for Enhanced RDP (RDS) Experience
Users who work in terminal sessions on an RDS (Remote Desktop Services) server often face a challenge with tiny UI elements making it hard to read. This problem is particularly evident for those using Full HD/HiDPI (Retina) monitors with high resolutions such as 2K and 4K. During an RDP session, users will find that the…