Introduction to Installing htop on CentOS 7
Many sysadmins know about top, the standard process management and activity monitor that comes on most Linux systems. But there are times when top does not provide the information you’re really looking for, or you want something that updates more frequently as the state of your system changes.
Look no further than htop. It’s interactive, real-time, and sports a variety of metrics and details above and beyond what top provides.
You can see CPU utilization at a glance, and that’s just the tip of the iceberg. Sort processes, kill rogue jobs right from htop, and set priorities. To learn more about htop, see the htop website.
Prerequisites to Installing htop on CentOS 7
To install htop on CentOS 7, you’ll need a few things:
- A CentOS 7 machine
- Basic knowledge of Linux and how to use the shell
Installing htop on CentOS 7: Two Methods
There are two different ways you can get htop on your computer. First, you can install it as a binary from your package manager (on CentOS this would be yum). This is a good option if you want to get it right away and don’t much mind what version of htop you’re getting.
You can also install htop from source. Since htop is open-source, you can download the code and build it yourself on your system. This takes a little longer, but you can be sure you’re getting the most updated build available (important if you’re looking for a specific new feature).
We’ll go through both methods step by step.
Install htop with Yum
The yum package manager does not contain htop by default. This is okay; we just need to add an EPEL repository so yum can find it. Here’s the commands to add that repository:
yum -y install epel-release
yum -y update
Now with the repository properly added, you can tell yum to install the htop process monitoring tool:
yum -y install htop
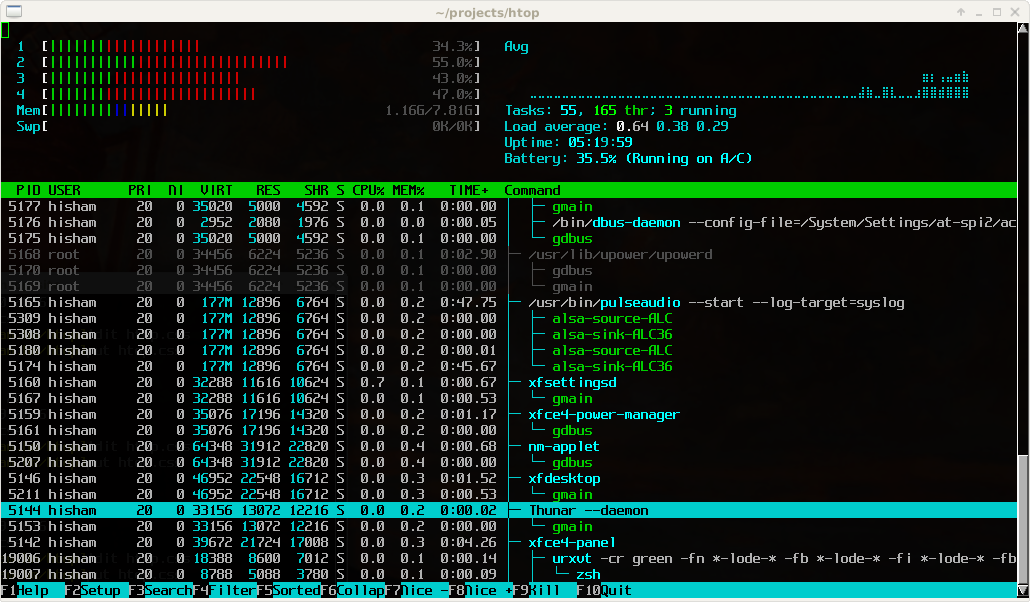
If the installation completes successfully, you should be able to type htop at the command line and see the status of your system.
(source: htop screenshots)
To learn more about htop’s features and how to customize it, see the htop website or htop explained.
Install htop from Source
To ensure you have the most recent version of htop and all the new features, you can install htop from source. This involves downloading the source code and building it on your machine.
Installing from source means you need to gather the dependencies yourself. Before we can install htop, we’ll need Development Tools (gcc and other compilers) and ncurses.
yum groupinstall “Development Tools”
yum install ncurses ncurses-devel
With the dependencies installed, we can grab the source code and extract it:
wget http://hisham.hm/htop/releases/2.0.2/htop-2.0.2.tar.gz
tar xvfvz htop-2.0.2.tar.gz
cd htop-2.0.2
Now that we’re in the folder with the htop source code, we can run these three commands to prepare and build the code:
./configure
make
make install
Once the make install step completes, you should be able to use htop. Try typing htop into your terminal and you should see the system monitor appear.
If you get a htop: command not found error, you’ll need to specify the location of the htop executable in your PATH.
Conclusion: htop on CentOS7 Installed
There’s so much you can do with htop, and we hope it will help monitor your processes more quickly and easily. As always, if you have questions please leave them in the comments below.