Category: Windows Server 2022
-
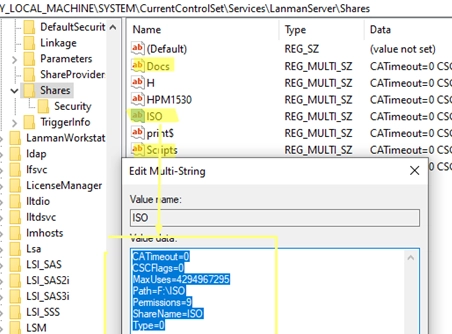
A Step-by-Step Guide to Migrating Your Existing Windows Shares to a New File Server
To migrate existing Windows shares to a new file server, you’ll need to utilize a combination of registry editing and file transfer methods. The shared network folders and their settings are stored under HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesLanmanServerShares in the Windows registry. Step-by-Step Guide for Migration: List Existing Shares:To view current shared SMB resources on a Windows host, use…
-

Troubleshooting an Unresponsive Start Menu on Windows Server RDS: A Comprehensive Guide
Occasionally, users encounter issues with the Start Menu or taskbar on RDS hosts utilizing Windows Server 2022 or 2019. Specifically, when a user clicks the Start button in a terminal session, the menu may fail to open, or the RDP session might freeze, rendering it unresponsive. The Start Menu and user interactions are driven by…
-
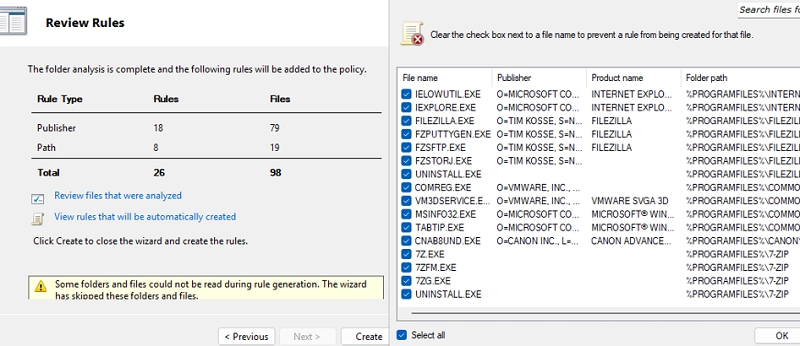
Mastering AppLocker: How to Configure Application Restriction Policies in Windows
Using AppLocker security policies, system administrators can manage which applications run on Windows systems. This tool allows for specific application restrictions, enabling designated user groups to execute applications while blocking others, such as standard users. Initially limited to the Enterprise editions, AppLocker is now accessible in Windows 10 Pro (from version 2004) and all versions…
-

Optimizing Performance: Resource Fair Sharing in Windows Server Remote Desktop Services (RDS)
A prevalent challenge with terminal servers that accommodate multiple users is the potential for one user to initiate a resource-heavy process, which can severely impact the performance of others. For instance, when a single user launches a process consuming over 90% of the CPU, it can render the server nearly unusable for other users. To…
-

Troubleshooting: Windows Stuck at ‘Getting Windows Ready, Don’t Turn Off Your Computer’ Screen
This issue of Windows getting stuck at the "Getting Windows Ready. Don’t turn off your computer" message is fairly common, especially on Windows Server versions (2022, 2019, 2016) and occasionally on Windows 10 and 11. This often occurs after installing updates or modifying system roles and features. When encountering this message, the best initial advice…
-
Optimizing DPI Scaling and Font Size for Enhanced RDP (RDS) Experience
Users who work in terminal sessions on an RDS (Remote Desktop Services) server often face a challenge with tiny UI elements making it hard to read. This problem is particularly evident for those using Full HD/HiDPI (Retina) monitors with high resolutions such as 2K and 4K. During an RDP session, users will find that the…
-

Tracking Program Installations and Removals: A Guide to Detecting User Actions on Windows
In enterprise environments with multiple administrators, tracking who installed or uninstalled software on Windows systems is crucial. To do this, you can extract information from the Windows Event Viewer logs. When applications are installed or uninstalled using the MSI installer, specific events are logged. The relevant event codes include: 11707: Indicates successful installation of an…
-
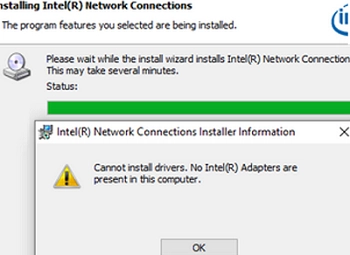
Troubleshooting Steps for Installing Network Adapter Drivers on Windows Server
When attempting to install Intel network drivers on Windows Server, users often encounter a common issue: the installer fails to recognize the Intel network adapter devices, leaving them appearing as unknown in Device Manager. The error message states that no Intel adapters are present, preventing any driver installation. This issue typically arises when Windows Server…
-
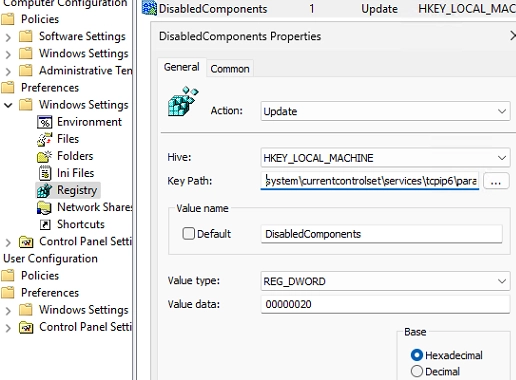
A Step-by-Step Guide to Prioritizing IPv4 over IPv6 in Windows Networks
By default, Windows attempts to connect to remote hosts using IPv6 if both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are available. This occurs when the DNS server or mDNS method returns both ‘AAAA’ (for IPv6) and ‘A’ (for IPv4) records. Such behavior may become problematic for network services or older applications that don’t support IPv6 or don’t…
-
How to Fix the “The Referenced Assembly Could Not Be Found” Error (0x80073701) on Windows
When working with Windows Server or Windows 10/11, you may encounter the error: The referenced assembly could not be found. Error: 0x80073701. This issue typically arises when adding or removing features or roles. A similar error may also appear when trying to enable optional features via PowerShell, such as the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL):…